That stuttering video call. The frozen game at the worst possible moment. The file upload that keeps failing at 95%. Behind these digital nightmares lies a silent killer: packet loss. It’s the internet equivalent of losing pieces of your mail in transit, except these lost pieces are carrying your data.
Unlike slow internet speeds that you can see coming, packet loss strikes randomly and ruthlessly. But here’s the good news: most packet loss is fixable with the right diagnostic approach and systematic troubleshooting. This guide will walk you through every proven method to hunt down and eliminate packet loss from your connection.
Before diving deep, let’s confirm you have packet loss:
- Gaming: Rubber-banding, teleporting players, unregistered hits
- Video Calls: Frozen frames, audio cutting out, “reconnecting” messages
- Streaming: Buffering despite good speed, quality drops
- General Use: Web pages partially loading, downloads failing
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, you likely have packet loss. Let’s fix it.
What Packet Loss Really Is
Imagine sending 100 letters through the mail, but only 97 arrive at their destination. That’s packet loss in the digital world. When you use the internet, your data travels in small units called “packets.” Each packet carries a piece of information, whether it’s part of a video frame, a game command, or a chunk of a file you’re downloading.
When packets fail to reach their destination, that’s packet loss. Unlike high ping (which means packets arrive slowly), packet loss means they don’t arrive at all. This distinction is crucial because the symptoms and fixes are different. A 200ms ping might make gaming feel sluggish, but 2% packet loss can make it unplayable.
The Journey of a Data Packet
Packet loss can occur at ANY point in this chain. Our job is to find where.
Step 1: Diagnose Where Packets Are Getting Lost
Before you can fix packet loss in games like Roblox, you need to know where it’s happening. This step is critical; randomly trying fixes without proper diagnosis wastes time and might not solve the real problem.
We’ll use three built-in tools to pinpoint packet loss. These work on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Tool 1: Ping Test (Quick General Check)
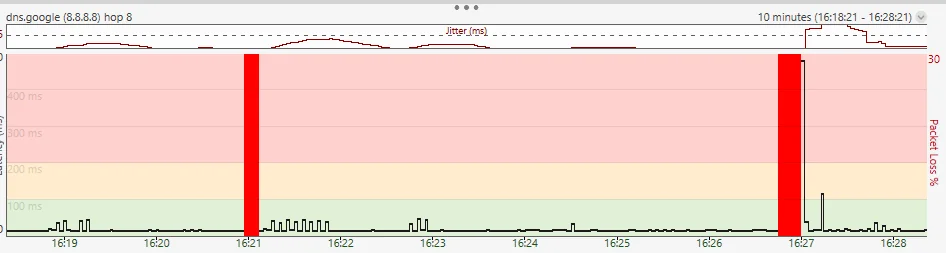
What to look for: Any packet loss above 1-2% is concerning. The example shows 4% loss, which would cause noticeable issues.
Tool 2: Traceroute (Find Where Loss Starts)
What to look for: Asterisks (*) indicate potential packet loss. If they appear at hop 1-2, it’s your local network. Mid-route suggests ISP issues.
Tool 3: Pathping (Detailed Analysis – Windows Only)
What to look for: Pathping shows exact loss percentages at each hop. Here, 10% loss starts at the ISP router.
Step 2: Fix Local Network Issues (Your Equipment)
If diagnostics show packet loss on the first few hops (your local network), or you want to rule out local issues first, start here. These fixes address the most common causes and are entirely within your control.
The Power Cycle Ritual
Correctly restarting your network equipment fixes many temporary issues.
- Unplug BOTH modem and router from power
- Wait 30 seconds (capacitors must discharge)
- Plug in modem FIRST, wait for all lights
- Then plug in router, wait 2 minutes
- Test connection with ethernet first
Cable Check
- Inspect ethernet cable for cuts, kinks, or damage
- Check connectors for bent pins or corrosion
- Try a different ethernet cable (Cat 5e or Cat 6)
- Test different ports on router
Switch to Ethernet
Wi-Fi is inherently unstable for real-time applications.
- Wi-Fi typically has higher latency than Ethernet
- Susceptible to interference from microwaves, Bluetooth
- Signal degrades through walls and distance
- Shared medium with all nearby networks
Router Firmware Update
- Find router IP (usually 192.168.1.1)
- Login to admin panel (check router sticker)
- Navigate to System/Administration/Update
- Check for and install latest firmware
- Never interrupt update process
Configure QoS (Quality of Service)
Prioritize gaming/work traffic over other activities.
- Access router admin interface
- Find QoS/Traffic Control settings
- Set gaming device to highest priority
- Or use “Gaming Mode” or SQM if available
- May need to disable “NAT Boost” first
Coax Cable Check (Cable Internet)
- Ensure tight connections at modem and wall
- Use RG6 cable, not older RG59
- Remove unnecessary splitters
- Direct line to modem is best
| Router Brand | QoS Menu Location | Key Setting |
|---|---|---|
| ASUS | Adaptive QoS > Gaming | Drag Gaming to top priority |
| Netgear | Dynamic QoS > Gaming | Enable and set bandwidth |
| TP-Link | Advanced > QoS | Add device rule, set high priority |
| Linksys | Priority > Devices | Set device to high priority |
| Amazon Eero | Network Settings > Eero Labs | Enable SQM / Optimize for Conferencing and Gaming |
Step 3: Optimize Your PC/Device Settings
Your computer or device can cause packet loss through software conflicts, resource competition, or misconfiguration. These fixes ensure your system isn’t sabotaging your connection.
Close Bandwidth-Hungry Applications
Background apps can saturate your connection, causing packet loss for everything else.
Windows Task Manager Check:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc
- Go to “Processes” tab
- Click “Network” column to sort by usage
- Close non-essential high-usage apps
Common Bandwidth Hogs to Check:
- Cloud storage sync (OneDrive, Dropbox, Google Drive)
- Torrent clients (even when “idle”)
- Game launchers downloading updates
- Multiple browser tabs with video/streaming
- Windows Update (pause during important tasks)
- Antivirus full system scans
Update Network Adapter Drivers
Outdated or corrupt drivers directly cause packet handling errors.
Windows Driver Update:
- Right-click Start Menu > Device Manager
- Expand “Network adapters”
- Right-click your adapter > “Update driver”
- Try automatic search first
- If that fails, visit manufacturer website for latest
Configure Firewall/Antivirus Exceptions
Security software can mistakenly block or delay legitimate packets.
Never disable your firewall completely. Instead, add specific exceptions for trusted applications. If testing requires temporary disabling, re-enable immediately after.
Add Game/App Exceptions:
- Windows Defender: Settings > Firewall > Allow an app
- Add your game executable (.exe file)
- Check both Private and Public network boxes
- For third-party antivirus, check their specific instructions
Step 4: Address ISP and Internet Path Issues
If your local network is clean but packet loss persists, the problem lies beyond your control, but not beyond your influence. Here’s how to identify and address ISP-related packet loss.
Gather Evidence Before Calling
ISPs handle countless “slow internet” complaints. Stand out with specific data:
Your ISP Packet Loss Report
- Pathping results showing loss at their network hops
- Multiple test times (morning, afternoon, evening)
- Different destination servers (proves it’s not one site)
- Your troubleshooting steps (shows you’ve done homework)
- Duration of issue (started Tuesday after storm, etc.)
Key Phrases That Get Results
- “I’m experiencing 10% packet loss starting at hop 4, which appears to be your network”
- “My pathping tests show consistent loss at [specific IP address]”
- “This is affecting real-time applications like video calls and gaming”
- “I’ve already tried [list your troubleshooting] on my end”
- “Can you check the line quality and signal levels from your end?”
- “Is there any known congestion or maintenance in my area?”
When to Escalate
If first-level support can’t help:
- Request escalation to “Level 2” or “Network Operations”
- Ask for a ticket number for tracking
- Request callbacks rather than waiting on hold
- Consider filing complaint with regulatory body if persistent
| Symptom | Likely Cause | ISP Should Check |
|---|---|---|
| Loss worse evenings/weekends | Network congestion | Node capacity, traffic shaping policies |
| Loss during rain/weather | Physical line damage | Cable integrity, connection points |
| Intermittent loss all day | Failing equipment | Modem signal levels, line noise |
| Loss to specific sites only | Peering/routing issues | BGP routes, peering agreements |
Step 5: Advanced Solutions for Persistent Packet Loss
When standard fixes fail, these advanced approaches can provide relief. They require more investment; either money, time, or technical expertise, but can solve stubborn packet loss issues.
When VPNs Help Packet Loss
VPNs can route around problem network paths.
VPNs CAN help if:
- Loss occurs in the “middle mile” (ISP to destination)
- Your ISP has poor routing to specific servers
- Packet loss is location/route specific
VPNs WON’T help if:
- Loss is in your local network
- Your ISP connection itself is bad
- Game servers are overloaded
Gaming-specific options: ExitLag, WTFast, Mudfish focus on game traffic optimization.
Signs You Need a New Router
- Daily reboots required for stability
- 5+ years old (lacks modern standards)
- Overheating even in open air
- Can’t handle your internet speed
- No SQM/QoS for bufferbloat
Key Features for Low Packet Loss
- SQM (Smart Queue Management) – Fights bufferbloat
- Powerful CPU – Handles packets without dropping
- Regular firmware updates – Security and fixes
- Good QoS implementation – Traffic prioritization
When to Call a Technician
- In-wall cable testing needed
- Physical line damage suspected
- Complex network setup required
- Business-critical connection
ISP Technician Visit Prep
- Document all test results
- Clear access to equipment
- Be present to explain issue
- Test together before they leave
Step 6: Test for Specific Issues – Bufferbloat and Hardware Failure
Two specific issues deserve special attention because they’re common but often overlooked: bufferbloat (which causes spikes under load) and failing network hardware.
Testing for Bufferbloat
Bufferbloat causes massive lag spikes when someone downloads/uploads large files.
Quick Bufferbloat Test
- Go to waveform.com/tools/bufferbloat
- Run the test (takes ~1 minute)
- Check your grade:
- A = No significant bufferbloat
- B = Some bufferbloat, may affect gaming
- C or lower = Severe bufferbloat, needs fixing
Fix for Bufferbloat:
- Enable SQM/Smart Queue Management on router
- Look for “Optimize for Gaming” settings
- Consider router with CAKE or FQ-CoDel algorithms
- Modern routers: Eero Pro 6, Netgear XR1000, IQrouter
Detecting Failing Network Card (NIC)
Your computer’s network adapter can fail, causing packet loss only on that device.
Symptoms of NIC Failure:
- Only one device has packet loss on network
- “Network cable unplugged” errors with good cable
- Intermittent disconnections
- Much slower speeds than other devices
- Device Manager shows yellow warning on adapter
Quick NIC Test:
- Test with USB network adapter ($15-30)
- If USB adapter works fine, internal NIC is failing
- For desktops: Install PCIe network card
- For laptops: Use USB adapter permanently
Maintaining a Stable Connection
Once you’ve fixed packet loss, keep it from returning with these maintenance practices. A little prevention saves hours of future troubleshooting.
- Check router firmware – Install updates for security and performance
- Run speed test – Ensure you’re getting what you pay for
- Clear dust from equipment – Overheating causes failures
- Test with ping/pathping – Catch issues early
- Review connected devices – Remove unknown/unused devices
- Check cable connections – Tighten any loose connectors
Network equipment in enclosed spaces or near heat sources fails prematurely. Ensure your modem and router have adequate ventilation. If they feel hot to touch, they need better airflow.
Packet Loss Symptoms to Solutions
| What You Experience | Likely Cause | Priority Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Gaming: Rubber-banding, teleporting | High packet loss (>2%) | Check local network first, then ISP path |
| Video calls freezing/dropping | Intermittent packet loss | Switch to ethernet, check bufferbloat |
| Lag when others use internet | Bufferbloat/No QoS | Enable QoS, consider SQM router |
| Worse at specific times | ISP congestion | Document and contact ISP with data |
| Only affects one device | Device-specific issue | Update drivers, check NIC health |
| Started after storm/construction | Physical line damage | ISP technician visit required |
Your Packet Loss Battle Plan
Packet loss transforms smooth internet experiences into frustrating battles with technology. But armed with proper diagnostic tools and systematic fixes, you can identify and eliminate most causes. Remember: packet loss is rarely mysterious; it’s almost always traceable to a specific point in your connection chain.
Start with diagnostics to pinpoint where packets disappear. Fix local issues first (they’re most common and entirely in your control). Work outward to ISP and internet path problems. Consider advanced solutions only after exhausting standard fixes. And once stable, maintain your network to prevent future issues.
The internet doesn’t have to be unreliable, especially during those sweaty Apex Legends sessions. With the right approach, you can achieve the stable, packet-loss-free connection that modern life demands. Your data deserves to arrive intact; now you know how to make that happen.
FAQs
Is 1% packet loss bad?
Yes, even 1% packet loss is noticeable in real-time applications. Gaming becomes frustrating at 1–2%, video calls suffer, and live streaming may buffer. For general browsing, you might not notice, but anything interactive will feel the impact.
Can packet loss be fixed permanently?
It depends on the cause. Local network issues (bad cables, Wi-Fi interference) can be permanently fixed. ISP infrastructure problems may require ongoing pressure to resolve. Internet routing issues can change daily. Regular maintenance prevents most recurring problems.
Why do I have packet loss with good internet speed?
Speed and packet loss are different issues. You can have a 1Gbps connection that drops 5% of packets. Speed tests measure bandwidth capacity; packet loss measures reliability. Think of it as a highway where speed is how many lanes, and packet loss is potholes.
Will a gaming router fix packet loss?
Only if your current router is the cause. A good gaming router with SQM can fix bufferbloat-related packet loss. QoS features help during network congestion. But it won’t fix ISP issues, bad cables, or Wi-Fi interference.
How do I know if my ISP is throttling me?
Run tests on various servers. If gaming/streaming shows loss but general sites don’t, or if it happens at certain data usage levels, suspect throttling.
Can Windows updates cause packet loss?
Yes. Windows updates can install problematic network drivers, reset network settings, or enable features that interfere with connections. If packet loss started after an update, try rolling back network drivers or the update itself.
Is packet loss worse on Wi-Fi 2.4GHz or 5GHz?
2.4GHz typically has more packet loss due to interference (microwaves, Bluetooth, neighbors) but better range. 5GHz has less interference but worse wall penetration. Both are inferior to Ethernet for preventing packet loss.
Should I use a VPN to fix packet loss?
Only in specific cases. VPNs can help if your ISP has poor routing to certain servers. They can’t fix local network problems or general ISP connection issues. Gaming VPNs (such as WTFast and ExitLag) are specifically designed for this use case.
How to fix 100% packet loss?
100% packet loss means that no data packets are being delivered, implying a total breakdown in communication across a network. To fix 100% packet loss, follow these steps: First, restart your router and modem. Then, use an Ethernet cable instead of Wi-Fi. Check cables for any loose connections or try others. Close apps that consume a lot of bandwidth. Lastly, contact your Internet Service Provider for assistance if the problem continues.






 Discord
Discord
 Instagram
Instagram
 Youtube
Youtube
 TikTok
TikTok