That number next to your name in the scoreboard. The reason you died behind cover. The difference between a headshot and shooting air. Ping is the invisible force that determines whether your online experience feels smooth or sluggish, yet most people don’t truly understand what it measures or how it works.
Like sonar pinging off a submarine, your computer sends out a signal and times how long the echo takes to return. This guide reveals everything about ping, from the network science behind those milliseconds to why some players seem to see the future while you’re stuck in the past.
How Ping Works: The Digital Echo
Your computer sends a signal and measures how long it takes to return
What is Ping? The Complete Definition
Ping is a network diagnostic tool that measures the round-trip time for data packets to travel between two points on a network. Named after the sound sonar makes when detecting objects underwater, ping sends out a digital “echo” and times how long it takes to hear back.
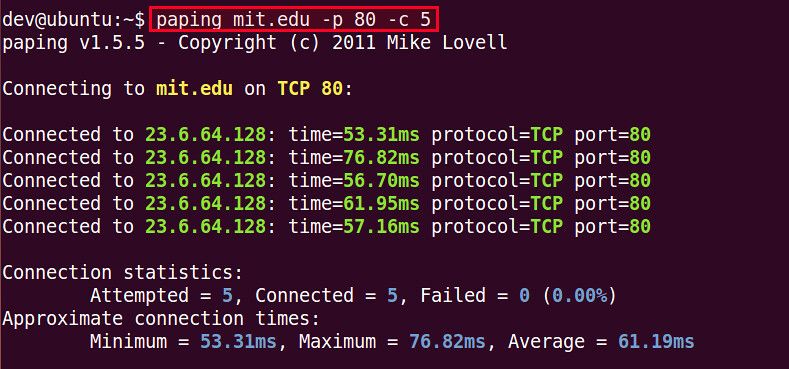
When you “ping” a server, your computer sends a small data packet called an ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Echo Request. If the server is online and reachable, it immediately sends back an Echo Reply. The time between sending and receiving, measured in milliseconds (ms), is your ping.
Understanding Ping Values: What’s Good, What’s Bad?
Ping values directly translate to user experience. Every millisecond of delay affects how responsive your connection feels, but what constitutes “good” ping depends entirely on what you’re doing online.
The Ping Spectrum: From Perfect to Problematic
Excellent
Good
Fair
Poor
How Ping Actually Works: The Technical Journey
The technical process behind ping helps explain why latency varies and what can go wrong. Here’s the complete journey of a ping packet through the internet:
Packet Creation
Your computer creates an ICMP Echo Request packet. This includes a unique identifier, sequence number, and timestamp. The packet is typically 32-56 bytes on Windows or 56-84 bytes on Linux/Mac.
Local Network Hop
The packet travels to your router/modem. This first hop often adds 1-5ms of latency. WiFi connections typically add more delay than ethernet due to signal processing and potential interference.
ISP Network
Your ISP routes the packet through their network. This may involve multiple routers and switches. Each hop decreases the TTL (Time To Live) value and adds latency.
Internet Backbone
Long-distance travel happens here. Packets may cross oceans via undersea cables (adding 50-100ms) or bounce between major internet exchange points. The physical distance creates unavoidable latency.
Destination Processing
The server receives the Echo Request and immediately generates an Echo Reply. The reply copies your original identifier and sequence number, then begins the return journey.
Round Trip Complete
Your computer receives the reply and calculates the time difference. This total Round-Trip Time (RTT) is displayed as your ping. The process repeats for continuous monitoring.
Ping in Gaming: Why Every Millisecond Counts
In online gaming, ping determines the delay between your actions and the server’s response. This creates different experiences across game genres, from barely noticeable delays to game-breaking lag.
How to Check Your Ping (All Platforms)
Testing your ping is simple but platform-specific. Here’s how to run ping tests on any device and interpret the results:
Reply from 142.250.185.78: bytes=32 time=27ms TTL=117
Reply from 142.250.185.78: bytes=32 time=29ms TTL=117
Reply from 142.250.185.78: bytes=32 time=28ms TTL=117
Ping statistics for 142.250.185.78:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 27ms, Maximum = 29ms, Average = 28ms
64 bytes from 142.250.185.78: icmp_seq=1 ttl=117 time=27.892 ms
64 bytes from 142.250.185.78: icmp_seq=2 ttl=117 time=29.234 ms
— google.com ping statistics —
3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 27.892/28.424/29.234/0.572 ms
1. Average Time: Your typical latency to the server. This is what most people call “ping.”
2. Packet Loss: Any loss above 0% indicates network problems. Even 1% loss severely impacts gaming.
3. Jitter (Standard Deviation): The consistency of your ping. High jitter means unstable connection.
TTL (Time To Live) shows how many network hops occurred. Windows starts at 128, Linux/Mac at 64. If you see TTL=117 from a Windows server, the packet went through approximately 11 routers (128-117).
Common Ping Problems and What They Mean
When ping tests fail or show poor results, the error messages and patterns reveal specific network issues. Understanding these helps you troubleshoot effectively.
Ping Error Message Decoder
| Error Message | What It Means | Common Causes | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request Timed Out | No reply received within timeout period (usually 4 seconds) |
• Target host is down • Firewall blocking ICMP • Network congestion • Routing issues |
• Verify target is online • Check firewall settings • Try different server • Test local network first |
| Destination Host Unreachable | Router can’t find path to destination |
• Target network down • Routing table issues • ARP resolution failed • Physical disconnection |
• Check physical connections • Restart router/modem • Verify IP address • Update network drivers |
| Unknown Host | DNS can’t resolve hostname to IP |
• DNS server issues • Typo in hostname • No internet connection • DNS cache corruption |
• Try ping with IP instead • Check DNS settings • Flush DNS cache • Try 8.8.8.8 (Google DNS) |
| TTL Expired in Transit | Packet died before reaching destination |
• Routing loop • Path too long • TTL set too low • Network misconfiguration |
• Increase TTL value • Run traceroute • Contact ISP • Check for routing loops |
| General Failure | Local network stack error |
• Network adapter issues • TCP/IP corruption • Driver problems • No network connection |
• Reset network adapter • Update drivers • Reset TCP/IP stack • Check cable/WiFi |
Factors That Affect Your Ping
Multiple factors influence ping times, from physical distance to network congestion. Understanding these helps set realistic expectations and identify improvement opportunities.
How to Reduce Your Ping: Practical Solutions
While you can’t break the laws of physics, many factors affecting ping are within your control. Here are proven methods to minimize latency:
Use Ethernet Instead of WiFi
The single most effective change. Ethernet eliminates WiFi processing delays, interference, and packet loss. Expect 5-20ms improvement plus rock-solid consistency.
Choose Closer Servers
Always pick game servers in your region. West Coast to East Coast USA adds 60-70ms. Europe to USA adds 100-150ms. Use server browsers when available.
Optimize Your Network
Close bandwidth-heavy applications. Streaming, downloads, and cloud backups compete for network resources. Enable QoS on your router to prioritize gaming traffic.
Update Network Drivers
Outdated network drivers can add unnecessary latency. Update both ethernet and WiFi drivers. Disable power saving features that might throttle network performance.
Consider ISP Upgrade
If ping remains high after optimization, your ISP routing might be the issue. Fiber typically offers the lowest latency. Some ISPs offer gaming-optimized routing.
Ping vs Other Network Metrics
Ping is just one measurement of network quality. Understanding related metrics provides a complete picture of your connection’s performance.
Jitter: Variation in ping over time. 30ms average with 5ms jitter is stable. 30ms with 50ms jitter causes stuttering.
Packet Loss: Percentage of packets that never arrive. Even 1% severely impacts gaming as lost data must be resent.
Bandwidth: Maximum data transfer rate (Mbps). Less important than ping for gaming but crucial for downloads/streaming.
Throughput: Actual data transfer achieved. Often lower than bandwidth due to network overhead.
Advanced Ping Concepts
Beyond basic ping tests, advanced users can leverage additional tools and techniques for deeper network analysis.
Conclusion
Ping measures the round-trip time for data to travel between your device and a server, directly impacting how responsive your internet feels. For gaming, video calls, and real-time applications, low ping matters more than raw bandwidth.
While physical distance creates unavoidable latency, many factors are within your control. Using ethernet instead of WiFi, choosing nearby servers, and optimizing your network can significantly reduce ping.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good ping for gaming?
Under 50ms is excellent for all game types. 50-100ms is acceptable for most games but noticeable in competitive shooters. Above 100ms creates significant delays that impact gameplay. Professional gamers aim for under 30ms, while casual gaming is fine up to 80ms.
Why is my ping high even with fast internet?
Bandwidth (internet speed) and latency (ping) are different metrics. High ping can result from physical distance to servers, network congestion, WiFi interference, poor routing by your ISP, or outdated network equipment. A 1Gbps connection can still have high ping if these factors aren’t optimized.
How do I check my ping?
Open Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac/Linux) and type “ping google.com” or any server address. In games, look for network statistics or ping display options, usually shown as a number followed by “ms” in the scoreboard or settings menu.
Can VPN reduce ping?
VPNs typically increase ping by adding extra routing steps. However, they might reduce ping in rare cases where your ISP has poor routing to game servers. Gaming VPNs optimize routes but still add 10-50ms overhead. Only use VPNs for gaming if you have specific routing issues.
What’s the difference between ping and latency?
Ping specifically refers to the round-trip time measured by the ping utility using ICMP packets. Latency is a broader term for any network delay. In gaming contexts, people use them interchangeably, but technically ping is one method of measuring latency.
Why does my ping spike randomly?
Ping spikes occur from network congestion, WiFi interference, background downloads/updates, other devices on your network streaming, ISP throttling, or overheating network equipment. Check for Windows updates, close streaming apps, and switch to ethernet to identify the cause.
Does ping affect download speed?
Ping doesn’t directly affect maximum download speed, but high ping can make downloads start slower and reduce efficiency. TCP/IP protocols wait for acknowledgments, so high latency means more waiting between data packets. This is why satellite internet with 600ms ping feels slow despite decent bandwidth.
What does 0% packet loss mean?
0% packet loss means every data packet sent reached its destination successfully. This is ideal. Any packet loss (even 1%) causes problems in gaming and video calls because lost data must be retransmitted, causing delays and stuttering. Consistent 0% packet loss indicates a healthy connection.
Can I improve ping on satellite internet?
Satellite internet has inherently high ping (500-700ms) due to the 70,000km round trip to geostationary satellites. This is a physics limitation that can’t be overcome. Low Earth Orbit satellites like Starlink reduce this to 20-40ms. For traditional satellite, consider alternative connections for gaming.
What ping do pro gamers use?
Professional gamers typically play with 1-30ms ping. Esports venues provide dedicated fiber connections to game servers. Online pros often relocate near server locations or use business-grade internet to maintain sub-30ms ping. Some leagues have maximum ping limits (usually 60-80ms) for competitive integrity.






 Discord
Discord
 Instagram
Instagram
 Youtube
Youtube
 TikTok
TikTok